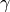hyperspy._components package¶
Submodules¶
hyperspy._components.arctan module¶
hyperspy._components.bleasdale module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.bleasdale.Bleasdale¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentBleasdale function component.
f(x) = (a+b*x)^(-1/c)
-
a¶ Float
-
b¶ Float
-
c¶ Float
-
function(x)¶
-
grad_a(x)¶ Returns d(function)/d(parameter_1)
-
grad_b(x)¶ Returns d(function)/d(parameter_1)
-
grad_c(x)¶ Returns d(function)/d(parameter_1)
-
hyperspy._components.eels_cl_edge module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.eels_cl_edge.EELSCLEdge(element_subshell, GOS=None)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentEELS core loss ionisation edge from hydrogenic or tabulated Hartree-Slater GOS with splines for fine structure fitting.
Hydrogenic GOS are limited to K and L shells.
Currently it only supports Peter Rez’s Hartree Slater cross sections parametrised as distributed by Gatan in their Digital Micrograph (DM) software. If Digital Micrograph is installed in the system HyperSpy in the standard location HyperSpy should find the path to the HS GOS folder. Otherwise, the location of the folder can be defined in HyperSpy preferences, which can be done through hs.preferences.gui() or the hs.preferences.EELS.eels_gos_files_path variable.
Parameters: - element_subshell ({str, dict}) – Usually a string, for example, ‘Ti_L3’ for the GOS of the titanium L3 subshell. If a dictionary is passed, it is assumed that Hartree Slater GOS was exported using GOS.as_dictionary, and will be reconstructed.
- GOS ({'hydrogenic', 'Hartree-Slater', None}) – The GOS to use. If None it will use the Hartree-Slater GOS if they are available, otherwise it will use the hydrogenic GOS.
-
onset_energy¶ Parameter – The edge onset position
-
intensity¶ Parameter – The factor by which the cross section is multiplied, what in favourable cases is proportional to the number of atoms of the element. It is a component.Parameter instance. It is fixed by default.
-
fine_structure_coeff¶ Parameter – The coefficients of the spline that fits the fine structure. Fix this parameter to fix the fine structure. It is a component.Parameter instance.
-
effective_angle¶ Parameter – The effective collection semi-angle. It is automatically calculated by set_microscope_parameters. It is a component.Parameter instance. It is fixed by default.
-
fine_structure_smoothing¶ float between 0 and 1 – Controls the level of smoothing of the fine structure model. Decreasing the value increases the level of smoothing.
-
fine_structure_active¶ bool – Activates/deactivates the fine structure feature.
-
E0¶
-
collection_angle¶
-
convergence_angle¶
-
fine_structure_active
-
fine_structure_coeff_to_txt(filename)¶
-
fine_structure_smoothing Controls the level of the smoothing of the fine structure.
It must a real number between 0 and 1. The higher close to 0 the higher the smoothing.
-
fine_structure_width¶
-
function(E)¶ Returns the number of counts in barns
-
get_fine_structure_as_signal1D()¶ Returns a spectrum containing the fine structure.
Notes
The fine structure is corrected from multiple scattering if the model was convolved with a low-loss spectrum
-
grad_intensity(E)¶
-
gui(display=True, toolkit=None, **kwargs)¶ Display or return interactive GUI element if available.
Parameters: - display (bool) – If True, display the user interface widgets. If False, return the widgets container in a dictionary, usually for customisation or testing.
- toolkit (str, iterable of strings or None) – If None (default), all available widgets are displayed or returned. If string, only the widgets of the selected toolkit are displayed if available. If an interable of toolkit strings, the widgets of all listed toolkits are displayed or returned.
-
set_microscope_parameters(E0, alpha, beta, energy_scale)¶ Parameters: - E0 (float) – Electron beam energy in keV.
- alpha (float) – Convergence semi-angle in mrad.
- beta (float) – Collection semi-angle in mrad.
- energy_scale (float) – The energy step in eV.
-
txt_to_fine_structure_coeff(filename)¶
hyperspy._components.eels_double_power_law module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.eels_double_power_law.DoublePowerLaw(A=1e-05, r=3.0, origin=0.0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.Component-
function(x)¶ Given an one dimensional array x containing the energies at which you want to evaluate the background model, returns the background model for the current parameters.
-
grad_A(x)¶
-
grad_origin(x)¶
-
grad_r(x)¶
-
grad_ratio(x)¶
-
grad_shift(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.eels_vignetting module¶
hyperspy._components.error_function module¶
hyperspy._components.exponential module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.exponential.Exponential¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentExponentian function components
f(x) = A*e^{-x/k}
Parameter Attribute A A k tau -
function(x)¶
-
grad_A(x)¶
-
grad_tau(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.expression module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.expression.Expression(expression, name, position=None, module='numpy', autodoc=True, add_rotation=False, rotation_center=None, **kwargs)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentCreate a component from a string expression.
-
compile_function(module='numpy', position=False)¶
-
hyperspy._components.gaussian module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.gaussian.Gaussian(A=1.0, sigma=1.0, centre=0.0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentNormalized gaussian function component
![f(x) = \frac{a}{\sqrt{2\pi c^{2}}}exp\left[-\frac{\left(x-b\right)^{2}}{2c^{2}}\right]](../_images/math/ffb4e9cfd8d6bec31cb985542093d3dbfe2b6c6b.png)
Parameter Attribute a A b centre c sigma For convenience the fwhm attribute can be used to get and set the full-with-half-maximum.
-
estimate_parameters(signal, x1, x2, only_current=False)¶ Estimate the gaussian by calculating the momenta.
Parameters: - signal (Signal1D instance) –
- x1 (float) – Defines the left limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- x2 (float) – Defines the right limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- only_current (bool) – If False estimates the parameters for the full dataset.
Returns: Return type: bool
Notes
Adapted from http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook/FittingData
Examples
>>> g = hs.model.components1D.Gaussian() >>> x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.01) >>> data = np.zeros((32, 32, 2000)) >>> data[:] = g.function(x).reshape((1, 1, 2000)) >>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D(data) >>> s.axes_manager._axes[-1].offset = -10 >>> s.axes_manager._axes[-1].scale = 0.01 >>> g.estimate_parameters(s, -10, 10, False)
-
function(x)¶
-
fwhm¶
-
grad_A(x)¶
-
grad_centre(x)¶
-
grad_sigma(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.gaussian2d module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.gaussian2d.Gaussian2D(A=1.0, sigma_x=1.0, sigma_y=1.0, centre_x=0.0, centre_y=0.0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentNormalized 2D elliptical gaussian function component
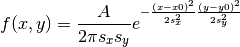
Parameter Attribute a amplitude x0,y0 centre s_x,s_y sigma -
function(x, y)¶
-
fwhm_x¶
-
fwhm_y¶
-
hyperspy._components.gaussianhf module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.gaussianhf.GaussianHF(height=1.0, fwhm=1.0, centre=0.0, **kwargs)¶ Bases:
hyperspy._components.expression.ExpressionNormalized gaussian function component, with a fwhm parameter instead of the sigma parameter, and a height parameter instead of the A parameter (scaling difference of sigma * sqrt(2*Pi)). This makes the parameter vs. peak maximum independent of sigma, and thereby makes locking of the parameter more viable. As long as there is no binning, the height parameter corresponds directly to the peak maximum, if not, the value is scaled by a linear constant (signal_axis.scale).
![f(x) = h \sqrt{2\pi}\mathrm{exp}{\left[-\frac{4 \log{2}\left(x-c\right)^{2}}{W^{2}}\right]}](../_images/math/763db485b5dda420953e18a6cd3fe1c97b7c9c8a.png)
Parameters: - height (float) – The height of the peak. If there is no binning, this corresponds directly to the maximum, otherwise the maximum divided by signal_axis.scale
- centre (float) – Location of the gaussian maximum, also the mean position.
- fwhm (float) – The full width half maximum value, i.e. the width of the gaussian at half the value of gaussian peak (at centre).
- **kwargs – Extra keyword arguments are passes to the
Expressioncomponent. An useful keyword argument that can be used to speed up the component is module. See theExpressioncomponent documentation for details.
The helper properties sigma and A are also defined for compatibility with Gaussian component.
See also
hyperspy.components.Gaussian-
A¶
-
estimate_parameters(signal, x1, x2, only_current=False)¶ Estimate the gaussian by calculating the momenta.
Parameters: - signal (Signal1D instance) –
- x1 (float) – Defines the left limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- x2 (float) – Defines the right limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- only_current (bool) – If False estimates the parameters for the full dataset.
Returns: Return type: bool
Notes
Adapted from http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook/FittingData
Examples
>>> g = hs.model.components1D.GaussianHF() >>> x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.01) >>> data = np.zeros((32, 32, 2000)) >>> data[:] = g.function(x).reshape((1, 1, 2000)) >>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D(data) >>> s.axes_manager._axes[-1].offset = -10 >>> s.axes_manager._axes[-1].scale = 0.01 >>> g.estimate_parameters(s, -10, 10, False)
-
integral_as_signal()¶ Utility function to get gaussian integral as Signal1D
-
sigma¶
hyperspy._components.heaviside module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.heaviside.HeavisideStep(A=1, n=0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentThe Heaviside step function
-
function(x)¶
-
grad_A(x)¶
-
grad_n(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.logistic module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.logistic.Logistic¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentLogistic function component
f(x) = a/(1+b*exp(-c*(x-origin)))
-
a¶ Float
-
b¶ Float
-
c¶ Float
-
origin¶ Float
-
function(x)¶
-
grad_a(x)¶ Returns d(function)/d(parameter_1)
-
grad_b(x)¶ Returns d(function)/d(parameter_1)
-
grad_c(x)¶ Returns d(function)/d(parameter_1)
-
grad_origin(x)¶ Returns d(function)/d(parameter_1)
-
hyperspy._components.lorentzian module¶
hyperspy._components.offset module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.offset.Offset(offset=0.0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentComponent to add a constant value in the y-axis
f(x) = k + x
Parameter Attribute k offset -
estimate_parameters(signal, x1, x2, only_current=False)¶ Estimate the parameters by the two area method
Parameters: - signal (BaseSignal instance) –
- x1 (float) – Defines the left limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- x2 (float) – Defines the right limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- only_current (bool) – If False estimates the parameters for the full dataset.
Returns: Return type: bool
-
function(x)¶
-
static
grad_offset(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.pes_core_line_shape module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.pes_core_line_shape.PESCoreLineShape(A=1.0, FWHM=1.0, origin=0.0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.Component-
function(x)¶ Given an one dimensional array x containing the energies at which you want to evaluate the background model, returns the background model for the current parameters.
-
grad_A(x)¶
-
grad_FWHM(x)¶
-
grad_ab(x)¶
-
grad_origin(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.pes_see module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.pes_see.SEE(A=1.0, Phi=1.0, B=0.0, sigma=0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentSecondary electron emission component for Photoemission Spectroscopy
-
A¶ float
-
Phi¶ float
-
B¶ float
-
sigma¶ float – Resolution parameter.
-
function(x)¶
-
grad_A(x)¶
-
grad_B(x)¶
-
grad_Phi(x)¶
-
grad_sigma(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.polynomial module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.polynomial.Polynomial(order=2)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.Componentn-order polynomial component.
Polynomial component defined by the coefficients parameters which is an array of len the order of the polynomial.
For example, the [1,2,3] coefficients define the following 3rd order polynomial: f(x) = 1x² + 2x + 3
-
coeffcients¶ array
-
estimate_parameters(signal, x1, x2, only_current=False)¶ Estimate the parameters by the two area method
Parameters: - signal (Signal1D instance) –
- x1 (float) – Defines the left limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- x2 (float) – Defines the right limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- only_current (bool) – If False estimates the parameters for the full dataset.
Returns: Return type: bool
-
function(x)¶
-
get_polynomial_order()¶
-
grad_coefficients(x)¶
-
grad_one_coefficient(x, index)¶ Returns the gradient of one coefficient
-
hyperspy._components.power_law module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.power_law.PowerLaw(A=1000000.0, r=3.0, origin=0.0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentPower law component
f(x) = A*(x-x0)^-r
Parameter Attribute A A r r x0 origin The left_cutoff parameter can be used to set a lower threshold from which the component will return 0.
-
estimate_parameters(signal, x1, x2, only_current=False, out=False)¶ Estimate the parameters by the two area method
Parameters: - signal (Signal1D instance) –
- x1 (float) – Defines the left limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- x2 (float) – Defines the right limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- only_current (bool) – If False, estimates the parameters for the full dataset.
- out (bool) – If True, returns the result arrays directly without storing in the parameter maps/values. The returned order is (A, r).
Returns: Return type: {bool, tuple of values}
-
function(x)¶
-
grad_A(x)¶
-
grad_origin(x)¶
-
grad_r(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.rc module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.rc.RC(V=1, V0=0, tau=1.0)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.Component-
function(x)¶
-
hyperspy._components.scalable_fixed_pattern module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.scalable_fixed_pattern.ScalableFixedPattern(signal1D, yscale=1.0, xscale=1.0, shift=0.0, interpolate=True)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentFixed pattern component with interpolation support.
f(x) = a*s(b*x-x0) + cParameter Attribute a yscale b xscale x0 shift The fixed pattern is defined by a single spectrum which must be provided to the ScalableFixedPattern constructor, e.g.:
In [1]: s = load('my_spectrum.hspy') In [2]: my_fixed_pattern = components.ScalableFixedPattern(s))
-
yscale, xscale, shift Float
-
interpolate¶ Bool – If False no interpolation is performed and only a y-scaled spectrum is returned.
-
prepare_interpolator : method to fine tune the interpolation
-
function(x)¶
-
grad_yscale(x)¶
-
gui(display=True, toolkit=None, **kwargs)¶ Display or return interactive GUI element if available.
Parameters: - display (bool) – If True, display the user interface widgets. If False, return the widgets container in a dictionary, usually for customisation or testing.
- toolkit (str, iterable of strings or None) – If None (default), all available widgets are displayed or returned. If string, only the widgets of the selected toolkit are displayed if available. If an interable of toolkit strings, the widgets of all listed toolkits are displayed or returned.
-
prepare_interpolator(kind='linear', fill_value=0, **kwargs)¶ Prepare interpolation.
Parameters: - x (array) – The spectral axis of the fixed pattern
- kind (str or int, optional) – Specifies the kind of interpolation as a string (‘linear’, ‘nearest’, ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic, ‘cubic’) or as an integer specifying the order of the spline interpolator to use. Default is ‘linear’.
- fill_value (float, optional) – If provided, then this value will be used to fill in for requested points outside of the data range. If not provided, then the default is NaN.
Notes
Any extra keyword argument is passed to scipy.interpolate.interp1d
-
hyperspy._components.voigt module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.voigt.Voigt¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentVoigt profile component with support for shirley background, non_isochromaticity,transmission_function corrections and spin orbit splitting specially suited for Photoemission spectroscopy data analysis.
f(x) = G(x)*L(x) where G(x) is the Gaussian function and L(x) is the Lorentzian function
-
area¶ Parameter
-
centre¶ Parameter
-
FWHM¶ Parameter
-
gamma¶ Parameter
-
resolution¶ Parameter
-
shirley_background¶ Parameter
-
non_isochromaticity¶ Parameter
-
transmission_function¶ Parameter
-
spin_orbit_splitting¶ Bool
-
spin_orbit_branching_ratio¶ float
-
spin_orbit_splitting_energy¶ float
-
estimate_parameters(signal, E1, E2, only_current=False)¶ Estimate the voigt function by calculating the momenta the gaussian.
Parameters: - signal (Signal1D instance) –
- x1 (float) – Defines the left limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- x2 (float) – Defines the right limit of the spectral range to use for the estimation.
- only_current (bool) – If False estimates the parameters for the full dataset.
Returns: Return type: bool
Notes
Adapted from http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook/FittingData
Examples
>>> g = hs.model.components1D.Gaussian() >>> x = np.arange(-10,10, 0.01) >>> data = np.zeros((32,32,2000)) >>> data[:] = g.function(x).reshape((1,1,2000)) >>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D({'data' : data}) >>> s.axes_manager.axes[-1].offset = -10 >>> s.axes_manager.axes[-1].scale = 0.01 >>> g.estimate_parameters(s, -10,10, False)
-
function(x)¶
-
-
hyperspy._components.voigt.voigt(x, FWHM=1, gamma=1, center=0, scale=1)¶ Voigt lineshape.
The voigt peak is the convolution of a Lorentz peak with a Gaussian peak.
The formula used to calculate this is:
z(x) = (x + 1j gamma) / (sqrt(2) sigma) w(z) = exp(-z**2) erfc(-1j z) / (sqrt(2 pi) sigma) V(x) = scale Re(w(z(x-center)))
Parameters: - gamma (real) – The half-width half-maximum of the Lorentzian
- FWHM (real) – The FWHM of the Gaussian
- center (real) – Location of the center of the peak
- scale (real) – Value at the highest point of the peak
Notes
Ref: W.I.F. David, J. Appl. Cryst. (1986). 19, 63-64
adjusted to use stddev and HWHM rather than FWHM parameters
hyperspy._components.volume_plasmon_drude module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.volume_plasmon_drude.VolumePlasmonDrude(intensity=1.0, plasmon_energy=15.0, fwhm=1.5)¶ Bases:
hyperspy.component.ComponentDrude volume plasmon energy loss function component, the energy loss function is defined as:
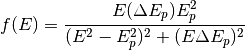
Parameter Attribute 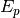
plasmon_energy 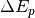
fwhm intensity intensity Notes
Refer to Egerton, R. F., Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy in the Electron Microscope, 2nd edition, Plenum Press 1996, pp. 154-158 for details, including original equations.
-
function(x)¶
-
grad_fwhm(x)¶
-
grad_intensity(x)¶
-
grad_plasmon_energy(x)¶
-
![f(x)=\frac{a}{\pi}\left[\frac{\gamma}{\left(x-x_{0}\right)^{2}+\gamma^{2}}\right]](../_images/math/2a9f2490c2b26cdce28d1ba212c8acc752a966fb.png)