hyperspy._components.gaussianhf module¶
-
class
hyperspy._components.gaussianhf.GaussianHF(height=1.0, fwhm=1.0, centre=0.0, module='numexpr', **kwargs)¶ Bases:
hyperspy._components.expression.ExpressionNormalized gaussian function component, with a fwhm parameter instead of the sigma parameter, and a height parameter instead of the A parameter (scaling difference of
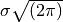 ).
This makes the parameter vs. peak maximum independent of
).
This makes the parameter vs. peak maximum independent of 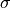 ,
and thereby makes locking of the parameter more viable. As long as there
is no binning, the height parameter corresponds directly to the peak
maximum, if not, the value is scaled by a linear constant
(signal_axis.scale).
,
and thereby makes locking of the parameter more viable. As long as there
is no binning, the height parameter corresponds directly to the peak
maximum, if not, the value is scaled by a linear constant
(signal_axis.scale).![f(x) = h\cdot\exp{\left[-\frac{4 \log{2}
\left(x-c\right)^{2}}{W^{2}}\right]}](../_images/math/06024dacb1ce895cee22dba0030c32520a488459.png)
Variable
Parameter
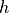
height
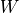
fwhm

centre
- Parameters
height (float) – The height of the peak. If there is no binning, this corresponds directly to the maximum, otherwise the maximum divided by signal_axis.scale
fwhm (float) – The full width half maximum value, i.e. the width of the gaussian at half the value of gaussian peak (at centre).
centre (float) – Location of the gaussian maximum, also the mean position.
**kwargs – Extra keyword arguments are passed to the
Expressioncomponent.
The helper properties sigma and A are also defined for compatibility with Gaussian component.
-
property
A¶
-
estimate_parameters(signal, x1, x2, only_current=False)¶ Estimate the gaussian by calculating the momenta.
- Parameters
- Returns
- Return type
Notes
Adapted from http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook/FittingData
Examples
>>> g = hs.model.components1D.GaussianHF() >>> x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.01) >>> data = np.zeros((32, 32, 2000)) >>> data[:] = g.function(x).reshape((1, 1, 2000)) >>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D(data) >>> s.axes_manager._axes[-1].offset = -10 >>> s.axes_manager._axes[-1].scale = 0.01 >>> g.estimate_parameters(s, -10, 10, False)
-
integral_as_signal()¶ Utility function to get gaussian integral as Signal1D
-
property
sigma¶