hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools module¶
Tools for working with distributions
-
class
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.KnuthF(data)¶ Bases:
objectClass which implements the function minimized by knuth_bin_width
- Parameters
data (array-like, one dimension) – data to be histogrammed
Notes
the function F is given by
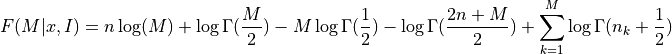
where
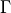 is the Gamma function,
is the Gamma function, 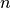 is the number of
data points,
is the number of
data points, 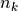 is the number of measurements in bin
is the number of measurements in bin 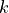 .
.See also
knuth_bin_width,astroML.plotting.hist-
bins(M)¶ Return the bin edges given a width dx
-
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.dasky_freedman_bin_width(data, return_bins=True)¶ Dask version of freedman_bin_width
- Parameters
data (dask array) – the data
return_bins (bool (optional)) – if True, then return the bin edges
- Returns
width (float) – optimal bin width using Scott’s rule
bins (ndarray) – bin edges: returned if return_bins is True
Notes
The optimal bin width is
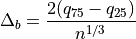
where
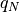 is the
is the 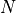 percent quartile of the data, and
percent quartile of the data, and
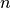 is the number of data points.
is the number of data points.
-
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.dasky_histogram(a, bins=10, **kwargs)¶ Enhanced histogram for dask arrays. The range keyword is ignored. Reads the data at most two times - once to determine best bins (if required), and second time to actually calculate the histogram.
- Parameters
- Returns
hist (array) – The values of the histogram. See normed and weights for a description of the possible semantics.
bin_edges (array of dtype float) – Return the bin edges
(length(hist)+1).
See also
-
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.dasky_scotts_bin_width(data, return_bins=True)¶ Dask version of scotts_bin_width
- Parameters
data (dask array) – the data
return_bins (bool (optional)) – if True, then return the bin edges
- Returns
width (float) – optimal bin width using Scott’s rule
bins (ndarray) – bin edges: returned if return_bins is True
Notes
The optimal bin width is:
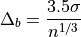
where
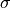 is the standard deviation of the data, and
is the standard deviation of the data, and
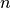 is the number of data points.
is the number of data points.
-
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.freedman_bin_width(data, return_bins=False)¶ Return the optimal histogram bin width using the Freedman-Diaconis rule
- Parameters
data (array-like, ndim=1) – observed (one-dimensional) data
return_bins (bool (optional)) – if True, then return the bin edges
- Returns
width (float) – optimal bin width using Scott’s rule
bins (ndarray) – bin edges: returned if return_bins is True
Notes
The optimal bin width is
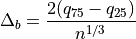
where
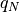 is the
is the 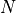 percent quartile of the data, and
percent quartile of the data, and
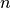 is the number of data points.
is the number of data points.
-
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.histogram(a, bins=10, range=None, **kwargs)¶ Enhanced histogram
This is a histogram function that enables the use of more sophisticated algorithms for determining bins. Aside from the bins argument allowing a string specified how bins are computed, the parameters are the same as numpy.histogram().
- Parameters
a (array_like) – array of data to be histogrammed
bins (int or list or str (optional)) – If bins is a string, then it must be one of: ‘blocks’ : use bayesian blocks for dynamic bin widths ‘knuth’ : use Knuth’s rule to determine bins ‘scotts’ : use Scott’s rule to determine bins ‘freedman’ : use the Freedman-diaconis rule to determine bins
range (tuple or None (optional)) – the minimum and maximum range for the histogram. If not specified, it will be (x.min(), x.max())
keyword arguments are described in numpy.hist() (other) –
- Returns
hist (array) – The values of the histogram. See normed and weights for a description of the possible semantics.
bin_edges (array of dtype float) – Return the bin edges
(length(hist)+1).
See also
-
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.knuth_bin_width(data, return_bins=False)¶ Return the optimal histogram bin width using Knuth’s rule 1
- Parameters
data (array-like, ndim=1) – observed (one-dimensional) data
return_bins (bool (optional)) – if True, then return the bin edges
- Returns
dx (float) – optimal bin width. Bins are measured starting at the first data point.
bins (ndarray) – bin edges: returned if return_bins is True
Notes
The optimal number of bins is the value M which maximizes the function
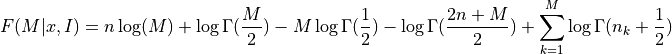
where
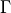 is the Gamma function,
is the Gamma function, 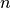 is the number of
data points,
is the number of
data points, 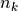 is the number of measurements in bin
is the number of measurements in bin 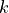 .
.References
- 1
Knuth, K.H. “Optimal Data-Based Binning for Histograms”. arXiv:0605197, 2006
See also
-
hyperspy.external.astroML.histtools.scotts_bin_width(data, return_bins=False)¶ Return the optimal histogram bin width using Scott’s rule:
- Parameters
data (array-like, ndim=1) – observed (one-dimensional) data
return_bins (bool (optional)) – if True, then return the bin edges
- Returns
width (float) – optimal bin width using Scott’s rule
bins (ndarray) – bin edges: returned if return_bins is True
Notes
The optimal bin width is
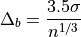
where
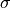 is the standard deviation of the data, and
is the standard deviation of the data, and
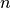 is the number of data points.
is the number of data points.