Signal2D Tools¶
The methods described in this section are only available for two-dimensional signals in the Signal2D class.
Two dimensional signal registration (alignment)¶
New in version 0.5.
The align2D() method provides
advanced image alignment functionality, including subpixel alignment.
Cropping an image¶
The crop_image() method crops the
image in-place e.g.:
>>> im = hs.datasets.example_signals.object_hologram()
>>> imc = im.crop(left=120, top=300, bottom=560) # im is cropped in-place
Cropping in HyperSpy is performed using the Signal indexing syntax. For example, to crop an image:
>>> im = hs.datasets.example_signals.object_hologram()
>>> # im is not cropped, imc is a "cropped view" of im
>>> imc = im.isig[120.:, 300.:560.]
It is possible to crop interactively using Region Of Interest (ROI). For example:
>>> im = hs.datasets.example_signals.object_hologram()
>>> roi = hs.roi.RectangularROI(left=120, right=460., top=300, bottom=560)
>>> im.plot()
>>> imc = roi.interactive(im)
>>> imc.plot()
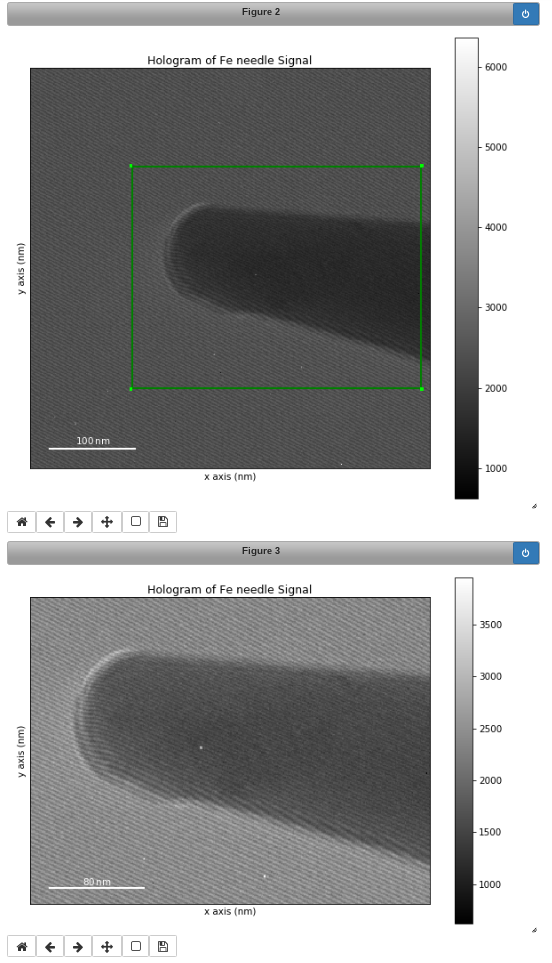
Interactive image cropping using a ROI.
Add a linear ramp¶
A linear ramp can be added to the signal via the
add_ramp() method. The parameters
ramp_x and ramp_y dictate the slope of the ramp in x- and y direction,
while the offset is determined by the offset parameter. The fulcrum of the
linear ramp is at the origin and the slopes are given in units of the axis
with the according scale taken into account. Both are available via the
AxesManager of the signal.