Working with big data
Warning
All the features described in this chapter are in beta state.
Although most of them work as described, their operation may not always be optimal, well-documented and/or consistent with their in-memory counterparts.
Therefore, although efforts will be taken to minimise major disruptions, the syntax and features described here may change in patch and minor HyperSpy releases. If you experience issues with HyperSpy’s lazy features please report them to the developers.
New in version 1.2.
HyperSpy makes it possible to analyse data larger than the available memory by
providing “lazy” versions of most of its signals and functions. In most cases
the syntax remains the same. This chapter describes how to work with data
larger than memory using the LazySignal class and
its derivatives.
Creating Lazy Signals
Lazy Signals from external data
If the data is large and not loaded by HyperSpy (for example a hdf5.Dataset
or similar), first wrap it in dask.array.Array as shown here and then pass it
as normal and call as_lazy():
>>> import h5py
>>> f = h5py.File("myfile.hdf5") # Load the file
>>> data = f['/data/path'] # Get the data
>>> import dask.array as da # Import dask to wrap
>>> chunks = (1000,100) # Chunk as appropriate
>>> x = da.from_array(data, chunks=chunks) # Wrap the data in dask
>>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D(x).as_lazy() # Create the lazy signal
Loading lazily
To load the data lazily, pass the keyword lazy=True. As an example,
loading a 34.9 GB .blo file on a regular laptop might look like:
>>> s = hs.load("shish26.02-6.blo", lazy=True)
>>> s
<LazySignal2D, title: , dimensions: (400, 333|512, 512)>
>>> s.data
dask.array<array-e..., shape=(333, 400, 512, 512), dtype=uint8, chunksize=(20, 12, 512, 512)>
>>> print(s.data.dtype, s.data.nbytes / 1e9)
uint8 34.9175808
>>> s.change_dtype("float") # To be able to perform decomposition, etc.
>>> print(s.data.dtype, s.data.nbytes / 1e9)
float64 279.3406464
Loading the dataset in the original unsigned integer format would require around 35GB of memory. To store it in a floating-point format one would need almost 280GB of memory. However, with the lazy processing both of these steps are near-instantaneous and require very little computational resources.
New in version 1.4: close_file()
Currently when loading an hdf5 file lazily the file remains open at
least while the signal exists. In order to close it explicitly, use the
close_file() method. Alternatively,
you could close it on calling compute()
by passing the keyword argument close_file=True e.g.:
>>> s = hs.load("file.hspy", lazy=True)
>>> ssum = s.sum(axis=0)
>>> ssum.compute(close_file=True) # closes the file.hspy file
Lazy stacking
Occasionally the full dataset consists of many smaller files. To combine them
into a one large LazySignal, we can stack them
lazily (both when loading or afterwards):
>>> siglist = hs.load("*.hdf5")
>>> s = hs.stack(siglist, lazy=True)
>>> # Or load lazily and stack afterwards:
>>> siglist = hs.load("*.hdf5", lazy=True)
>>> s = hs.stack(siglist) # no need to pass 'lazy', as signals already lazy
>>> # Or do everything in one go:
>>> s = hs.load("*.hdf5", lazy=True, stack=True)
Casting signals as lazy
To convert a regular HyperSpy signal to a lazy one such that any future
operations are only performed lazily, use the
as_lazy() method:
>>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D(np.arange(150.).reshape((3, 50)))
>>> s
<Signal1D, title: , dimensions: (3|50)>
>>> sl = s.as_lazy()
>>> sl
<LazySignal1D, title: , dimensions: (3|50)>
Machine learning
Decomposition algorithms for machine learning often perform
large matrix manipulations, requiring significantly more memory than the data size.
To perform decomposition operation lazily, HyperSpy provides access to several “online”
algorithms as well as dask’s lazy SVD algorithm.
Online algorithms perform the decomposition by operating serially on chunks of
data, enabling the lazy decomposition of large datasets. In line with the
standard HyperSpy signals, lazy decomposition()
offers the following online algorithms:
Algorithm |
Method |
|---|---|
“SVD” (default) |
|
“PCA” |
|
“ORPCA” |
|
“ORNMF” |
See also
decomposition() for more details on decomposition
with non-lazy signals.
GPU support
Lazy data processing on GPUs requires explicitly transferring the data to the GPU.
On linux, it is recommended to use the dask_cuda library (not supported on windows) to manage the dask scheduler. As for CPU lazy processing, if the dask scheduler is not specified, the default scheduler will be used.
>>> from dask_cuda import LocalCUDACluster
>>> from dask.distributed import Client
>>> cluster = LocalCUDACluster()
>>> client = Client(cluster)
>>> import hyperspy.api as hs
>>> import cupy as cp
>>> import dask.array as da
>>> # Create a dask array
>>> data = da.random.random(size=(20, 20, 100, 100))
>>> print(data)
... dask.array<random_sample, shape=(20, 20, 100, 100), dtype=float64,
... chunksize=(20, 20, 100, 100), chunktype=numpy.ndarray>
>>> # convert the dask chunks from numpy array to cupy array
>>> data = data.map_blocks(cp.asarray)
>>> print(data)
... dask.array<random_sample, shape=(20, 20, 100, 100), dtype=float64,
... chunksize=(20, 20, 100, 100), chunktype=cupy.ndarray>
>>> # Create the signal
>>> s = hs.signals.Signal2D(data).as_lazy()
Note
See the dask blog on Richardson Lucy (RL) deconvolution for an example of lazy processing on GPUs using dask and cupy
Model fitting
Most curve-fitting functionality will automatically work on models created from lazily loaded signals. HyperSpy extracts the relevant chunk from the signal and fits to that.
The linear 'lstsq' optimizer supports fitting the entire dataset in a vectorised manner
using dask.array.linalg.lstsq(). This can give potentially enormous performance benefits over fitting
with a nonlinear fitter, but comes with the restrictions explained in the linear fitting section.
Practical tips
Despite the limitations detailed below, most HyperSpy operations can be performed lazily. Important points are:
Chunking
Data saved in the HDF5 format is typically divided into smaller chunks which can be loaded separately into memory,
allowing lazy loading. Chunk size can dramatically affect the speed of various HyperSpy algorithms, so chunk size is
worth careful consideration when saving a signal. HyperSpy’s default chunking sizes are probably not optimal
for a given data analysis technique. For more comprehensible documentation on chunking,
see the dask array chunks and best practices docs. The chunks saved into HDF5 will
match the dask array chunks in s.data.chunks when lazy loading.
Chunk shape should follow the axes order of the numpy shape (s.data.shape), not the hyperspy shape.
The following example shows how to chunk one of the two navigation dimensions into smaller chunks:
>>> import dask.array as da
>>> data = da.random.random((10, 200, 300))
>>> data.chunksize
(10, 200, 300)
>>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D(data).as_lazy()
>>> s # Note the reversed order of navigation dimensions
<LazSignal1D, title: , dimensions: (200, 10|300)>
>>> s.save('chunked_signal.hspy', chunks=(10, 100, 300)) # Chunking first hyperspy dimension (second array dimension)
>>> s2 = hs.load('chunked_signal.hspy', lazy=True)
>>> s2.data.chunksize
(10, 100, 300)
To get the chunk size of given axes, the get_chunk_size()
method can be used:
>>> import dask.array as da
>>> data = da.random.random((10, 200, 300))
>>> data.chunksize
(10, 200, 300)
>>> s = hs.signals.Signal1D(data).as_lazy()
>>> s.get_chunk_size() # All navigation axes
((10,), (200,))
>>> s.get_chunk_size(0) # The first navigation axis
((200,),)
New in version 1.3.2.
By default, HyperSpy tries to optimize the chunking for most operations. However,
it is sometimes possible to manually set a more optimal chunking manually. Therefore,
many operations take a rechunk or optimize keyword argument to disable
automatic rechunking.
New in version 1.7.0.
For more recent versions of dask (dask>2021.11) when using hyperspy in a jupyter notebook a helpful html representation is available.
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import hyperspy.api as hs
>>> data = np.zeros((20, 20, 10, 10, 10))
>>> s = hs.signals.Signal2D(data)
>>> s
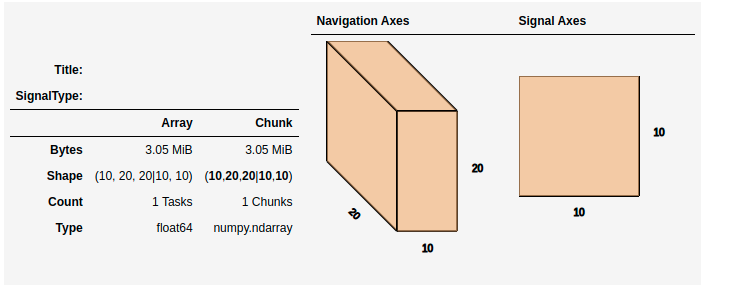
This helps to visualize the chunk structure and identify axes where the chunk spans the entire axis (bolded axes).
Computing lazy signals
Upon saving lazy signals, the result of computations is stored on disk.
In order to store the lazy signal in memory (i.e. make it a normal HyperSpy
signal) it has a compute() method:
>>> s
<LazySignal2D, title: , dimensions: (|512, 512)>
>>> s.compute()
[########################################] | 100% Completed | 0.1s
>>> s
<Signal2D, title: , dimensions: (|512, 512)>
Lazy operations that affect the axes
When using lazy signals the computation of the data is delayed until
requested. However, the changes to the axes properties are performed
when running a given function that modfies them i.e. they are not
performed lazily. This can lead to hard to debug issues when the result
of a given function that is computed lazily depends on the value of the
axes parameters that may have changed before the computation is requested.
Therefore, in order to avoid such issues, it is reccomended to explicitly
compute the result of all functions that are affected by the axes
parameters. This is the reason why e.g. the result of
shift1D() is not lazy.
Limitations
Most operations can be performed lazily. However, lazy operations come with a few limitations and constraints that we detail below.
Immutable signals
An important limitation when using LazySignal is the inability to modify
existing data (immutability). This is a logical consequence of the DAG (tree
structure, explained in Behind the scenes –technical details), where a complete history of the
processing has to be stored to traverse later.
In fact, lazy evaluation removes the need for such operation, since only additional tree branches are added, requiring very little resources. In practical terms the following fails with lazy signals:
>>> s = hs.signals.BaseSignal([0]).as_lazy()
>>> s += 1
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-6-1bd1db4187be>", line 1, in <module>
s += 1
File "<string>", line 2, in __iadd__
File "/home/fjd29/Python/hyperspy3/hyperspy/signal.py", line 1591, in _binary_operator_ruler
getattr(self.data, op_name)(other)
AttributeError: 'Array' object has no attribute '__iadd__'
However, when operating lazily there is no clear benefit to using in-place operations. So, the operation above could be rewritten as follows:
>>> s = hs.signals.BaseSignal([0]).as_lazy()
>>> s = s + 1
Or even better:
>>> s = hs.signals.BaseSignal([0]).as_lazy()
>>> s1 = s + 1
Other minor differences
Histograms for a
LazySignaldo not supportknuthandblocksbinning algorithms.CircleROI sets the elements outside the ROI to
np.naninstead of using a masked array, becausedaskdoes not support masking. As a convenience,nansum,nanmeanand othernan*signal methods were added to mimic the workflow as closely as possible.
Saving Big Data
The most efficient format supported by HyperSpy to write data is the zspy format, mainly because it supports writing currently from concurrently from multiple threads or processes. This also allows for smooth interaction with dask-distributed for efficient scaling.
Behind the scenes –technical details
Standard HyperSpy signals load the data into memory for fast access and processing. While this behaviour gives good performance in terms of speed, it obviously requires at least as much computer memory as the dataset, and often twice that to store the results of subsequent computations. This can become a significant problem when processing very large datasets on consumer-oriented hardware.
HyperSpy offers a solution for this problem by including
LazySignal and its derivatives. The main idea of
these classes is to perform any operation (as the name suggests)
lazily (delaying the
execution until the result is requested (e.g. saved, plotted)) and in a
blocked fashion. This is
achieved by building a “history tree” (formally called a Directed Acyclic Graph
(DAG)) of the computations, where the original data is at the root, and any
further operations branch from it. Only when a certain branch result is
requested, the way to the root is found and evaluated in the correct sequence
on the correct blocks.
The “magic” is performed by (for the sake of simplicity) storing the data not
as numpy.ndarray, but dask.array.Array (see the
dask documentation). dask
offers a couple of advantages:
Arbitrary-sized data processing is possible. By only loading a couple of chunks at a time, theoretically any signal can be processed, albeit slower. In practice, this may be limited: (i) some operations may require certain chunking pattern, which may still saturate memory; (ii) many chunks should fit into the computer memory comfortably at the same time.
Loading only the required data. If a certain part (chunk) of the data is not required for the final result, it will not be loaded at all, saving time and resources.
Able to extend to a distributed computing environment (clusters). :py:
dask.distributed(see the dask documentation) offers a straightforward way to expand the effective memory for computations to that of a cluster, which allows performing the operations significantly faster than on a single machine.