Signal1D Tools
The methods described in this section are only available for one-dimensional signals in the Signal1D class.
Cropping
The crop_signal1D() crops the
spectral energy range in-place. If no parameter is passed, a user interface
appears in which to crop the one dimensional signal. For example:
s = hs.datasets.example_signals.EDS_TEM_Spectrum()
s.crop_signal1D(5, 15) # s is cropped in place
Additionally, cropping in HyperSpy can be performed using the Signal indexing syntax. For example, the following crops a spectrum to the 5 keV-15 keV region:
s = hs.datasets.example_signals.EDS_TEM_Spectrum()
sc = s.isig[5.:15.] # s is not cropped, sc is a "cropped view" of s
It is possible to crop interactively using Region Of Interest (ROI). For example:
s = hs.datasets.example_signals.EDS_TEM_Spectrum()
roi = hs.roi.SpanROI(left=5, right=15)
s.plot()
sc = roi.interactive(s)
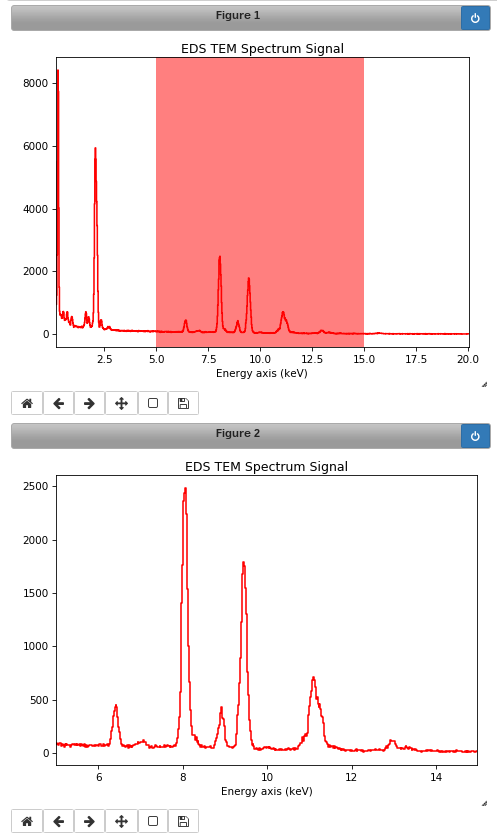
Interactive spectrum cropping using a ROI.
Background removal
New in version 1.4: zero_fill and plot_remainder keyword arguments and big speed
improvements.
The remove_background() method provides
background removal capabilities through both a CLI and a GUI. The GUI displays
an interactive preview of the remainder after background subtraction. Currently,
the following background types are supported: Doniach, Exponential, Gaussian,
Lorentzian, Polynomial, Power law (default), Offset, Skew normal, Split Voigt
and Voigt. By default, the background parameters are estimated using analytical
approximations (keyword argument fast=True). The fast option is not accurate
for most background types - except Gaussian, Offset and Power law -
but it is useful to estimate the initial fitting parameters before performing a
full fit. For better accuracy, but higher processing time, the parameters can
be estimated using curve fitting by setting fast=False.
Example of usage:
s = hs.datasets.artificial_data.get_core_loss_eels_signal(add_powerlaw=True)
s.remove_background(zero_fill=False)
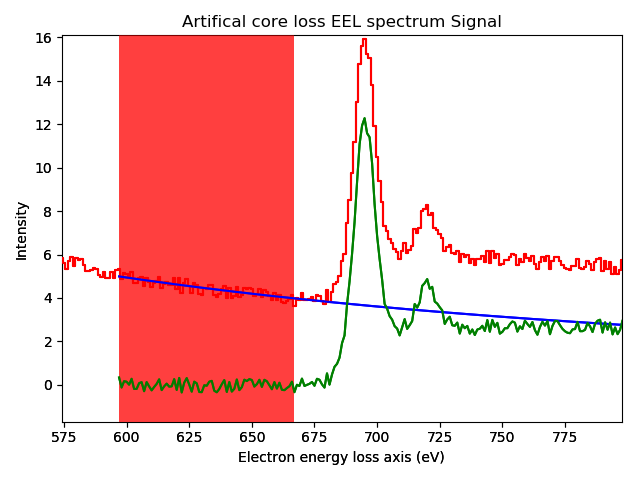
Interactive background removal. In order to select the region used to estimate the background parameters (red area in the figure) click inside the axes of the figure and drag to the right without releasing the button.
Calibration
The calibrate() method provides a user
interface to calibrate the spectral axis.
Alignment
The following methods use sub-pixel cross-correlation or user-provided shifts to align spectra. They support applying the same transformation to multiple files.
Integration
Deprecated since version 1.3: integrate_in_range().
It will be removed in 2.0. Use integrate1D()
instead, possibly in combination with a Region Of Interest (ROI) if interactivity
is required.
Data smoothing
The following methods (that include user interfaces when no arguments are passed) can perform data smoothing with different algorithms:
smooth_lowess()(requiresstatsmodelsto be installed)
Spike removal
spikes_removal_tool() provides an user
interface to remove spikes from spectra. The derivative histogram allows to
identify the appropriate threshold.
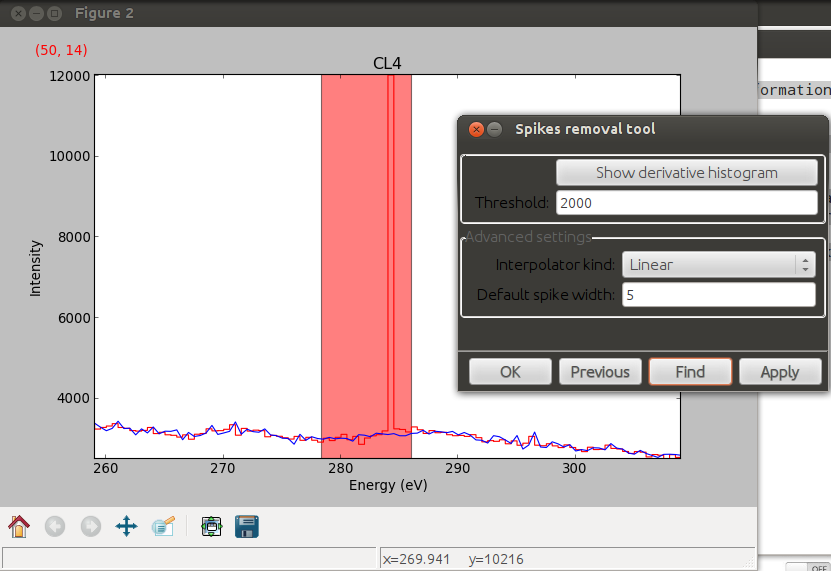
Spikes removal tool.
Peak finding
A peak finding routine based on the work of T. O’Haver is available in HyperSpy
through the find_peaks1D_ohaver()
method.
Other methods
Interpolate the spectra in between two positions
interpolate_in_between()Convolve the spectra with a gaussian
gaussian_filter()Apply a hanning taper to the spectra
hanning_taper()