Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Component convolution#
This example illustrates the convolution steps in the implementation of convolution in model fitting.
import hyperspy.api as hs
import numpy as np
from hyperspy.misc.axis_tools import calculate_convolution1D_axis
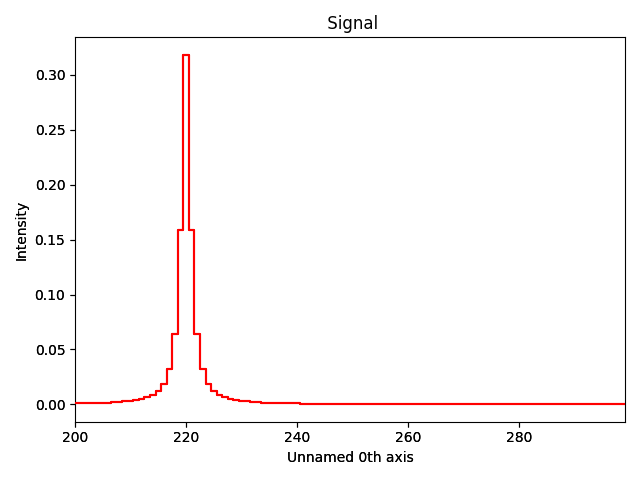
Create a signal containing a Lorentzian peak:
f = hs.model.components1D.Lorentzian(centre=220)
f_signal = hs.signals.Signal1D(f.function(np.arange(200, 300)))
f_signal.axes_manager.signal_axes.set(offset=200)
f_signal.plot()
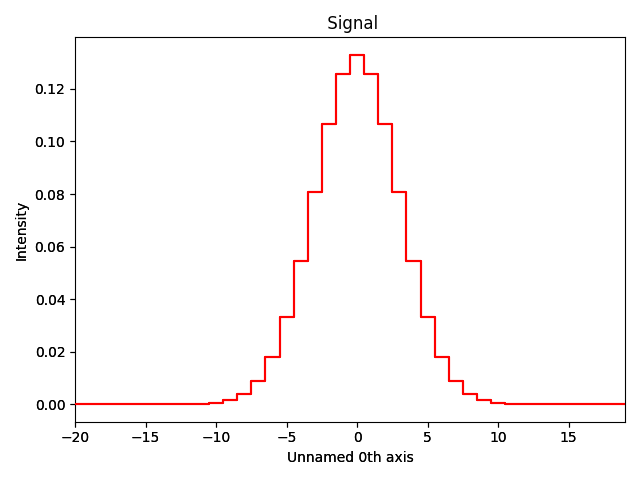
Create a second signal, for example a detector response:
g = hs.model.components1D.Gaussian(sigma=3)
g_signal = hs.signals.Signal1D(g.function(np.arange(-20, 20)))
g_signal.axes_manager.signal_axes.set(offset=-20)
g_signal.plot()
Create the “convolution axis” which adds the necessary padding:
convolution_axis = calculate_convolution1D_axis(
f_signal.axes_manager.signal_axes[0], g_signal.axes_manager.signal_axes[0]
)
Extend the data over the full range of the “convolution axis” and take the
convolution with g_signal:
f_padded_data = f.function(convolution_axis)
convolved_data = np.convolve(f_padded_data, g_signal.data, mode="valid")
convolved_signal = hs.signals.Signal1D(convolved_data)
convolved_signal.axes_manager.signal_axes.set(offset=f_signal.axes_manager[-1].offset)
Display the comparison of both signals:
hs.plot.plot_spectra([f_signal, convolved_signal])
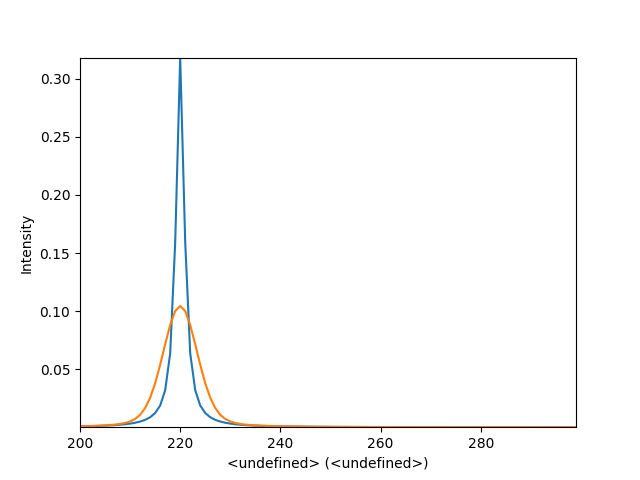
<Axes: xlabel='<undefined> (<undefined>)', ylabel='Intensity'>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.804 seconds)