Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Combine PolygonROI#
Combine several PolygonROI.
import hyperspy.api as hs
Create a signal:
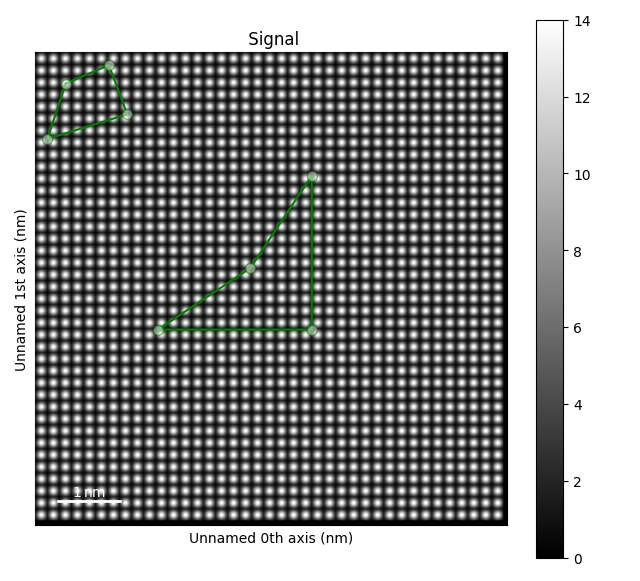
Create the ROIs, here PolygonROI:
roi = hs.roi.PolygonROI([(2, 4.5), (4.5, 4.5), (4.5, 2), (3.5, 3.5)])
roi2 = hs.roi.PolygonROI([(0.5, 0.5), (1.2, 0.2), (1.5, 1), (0.2, 1.4)])
We plot the signal add the ROIs to the figure using add_widget().
s.plot()
roi.add_widget(s, axes=s.axes_manager.signal_axes)
roi2.add_widget(s, axes=s.axes_manager.signal_axes)
<hyperspy.drawing._widgets.polygon.PolygonWidget object at 0x7f52d7c5eae0>
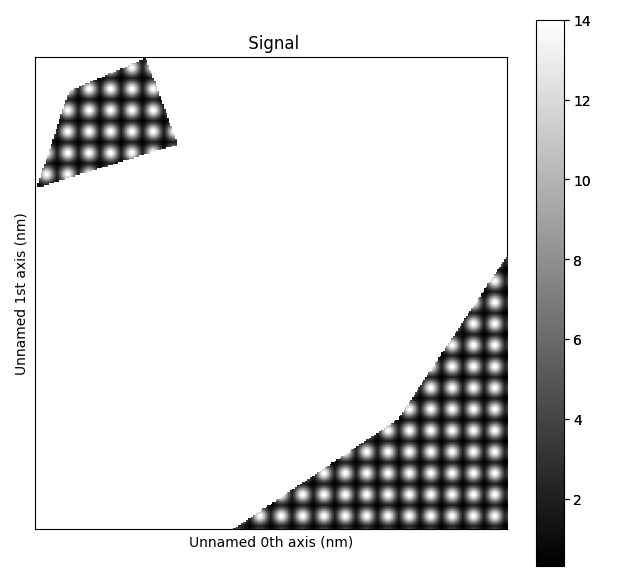
Now that we have two ROIs, roi and roi2, we can combine them to slice a signal
by using the following function:
s_roi_combined = hs.roi.combine_rois(s, [roi, roi2])
s_roi_combined.plot()
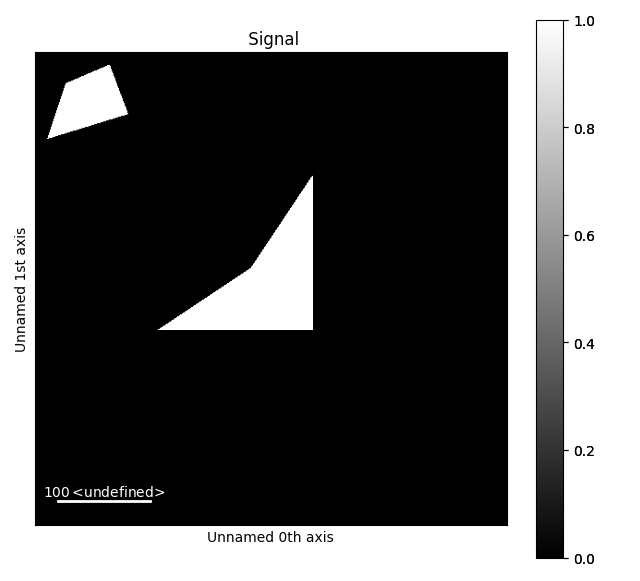
It is also possible to get a boolean mask from the ROIs, which can be useful for
interacting with other libraries. You need to supply the signal’s axes_manager
to get the correct parameters for creating the mask:
boolean_mask = hs.roi.mask_from_rois([roi, roi2], s.axes_manager)
boolean_mask = hs.signals.Signal2D(boolean_mask)
boolean_mask.plot()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.797 seconds)